Publications
P. M. Lenggenhager, M. M. Denner, D. E. Gökmen, M. Koch-Janusz, T. Neupert, M. H. Fischer
P. M. Lenggenhager, M. M. Denner, D. E. Gökmen, M. Koch-Janusz, T. Neupert, M. H. Fischer
arXiv:2510.02466 (2025)
– Uploaded 06 Oct 2025
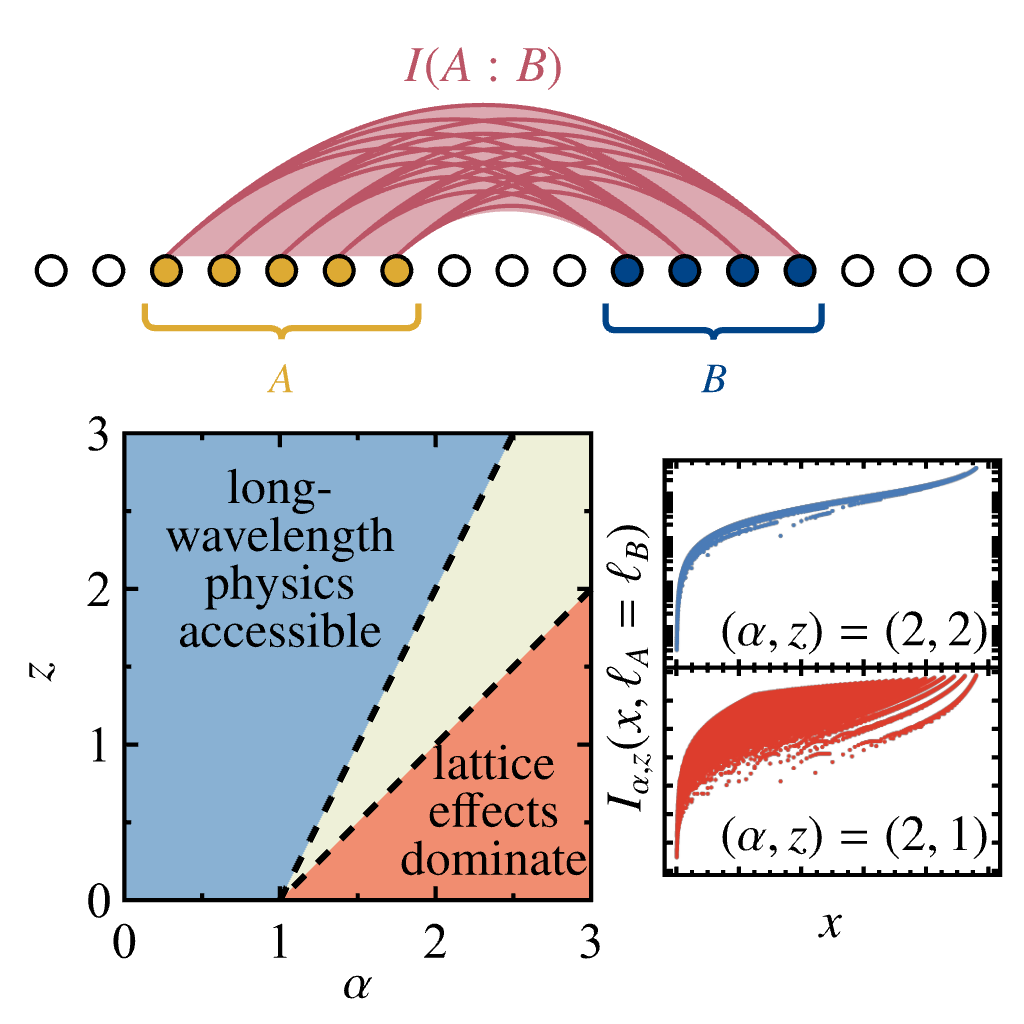
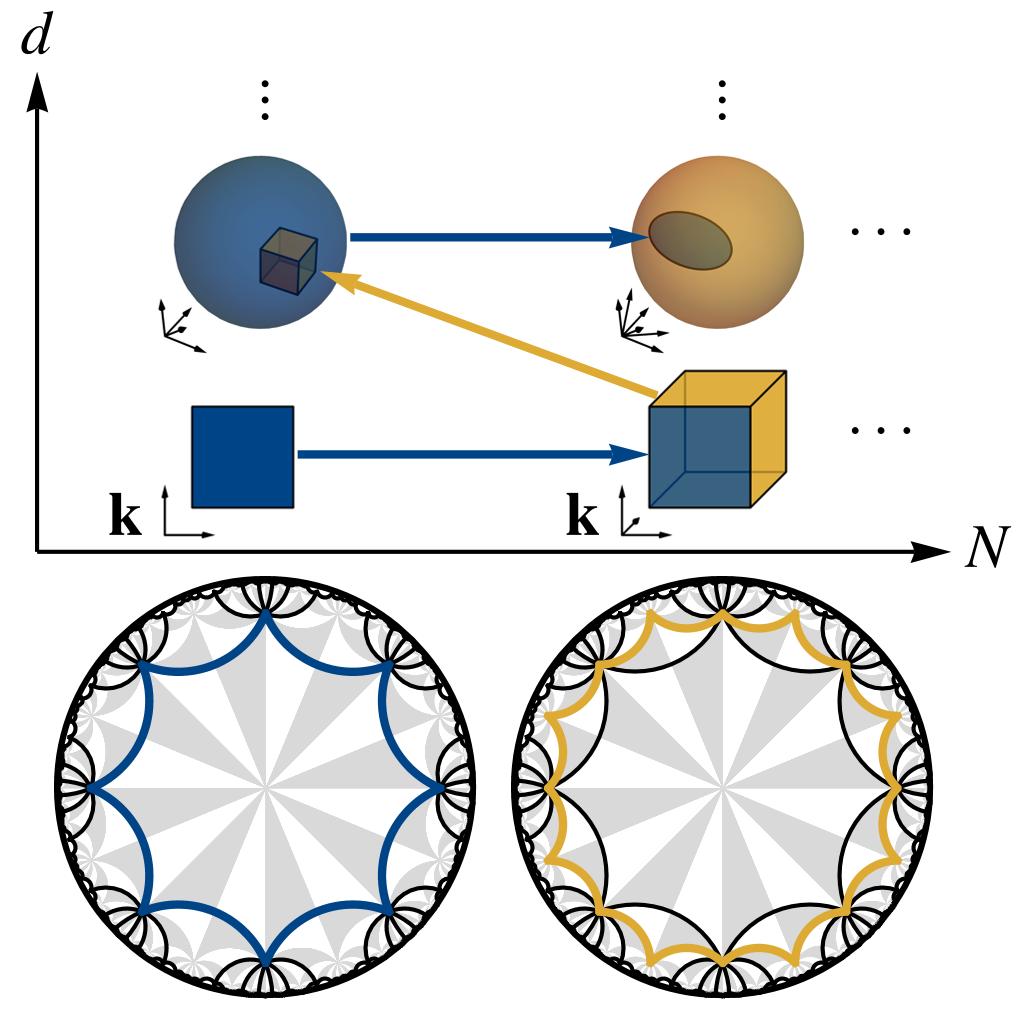
Quantum mutual information is an important tool for characterizing correlations in quantum many-body systems, but its numerical evaluation is often prohibitively expensive. While some variants of Rényi Mutual Information (RMI) are computationally more tractable, it is not clear whether they correctly capture the long-wavelength physics or are dominated by UV effects, which is of key importance in lattice simulations. We analyze the relevance of lattice effects on the family of α-z Rényi mutual informations for ground states of models with conformal field theory descriptions. On the example of massless free fermions we identify distinct regions in the α-z plane, where RMI corrections due to the lattice are relevant or irrelevant. We further support these findings with MPS calculations on the transverse field Ising model (TFIM). Our results, accompanied by the open-source Julia package QMICalc.jl, provide guidance to using RMI in quantum-many body physics numerical computations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, M. M. Denner, D. E. Gökmen, M. Koch-Janusz, T. Neupert, M. H. Fischer
P. M. Lenggenhager, M. M. Denner, D. E. Gökmen, M. Koch-Janusz, T. Neupert, M. H. Fischer
arXiv:2510.02466 (2025)
– Uploaded 06 Oct 2025
Quantum mutual information is an important tool for characterizing correlations in quantum many-body systems, but its numerical evaluation is often prohibitively expensive. While some variants of Rényi Mutual Information (RMI) are computationally more tractable, it is not clear whether they correctly capture the long-wavelength physics or are dominated by UV effects, which is of key importance in lattice simulations. We analyze the relevance of lattice effects on the family of α-z Rényi mutual informations for ground states of models with conformal field theory descriptions. On the example of massless free fermions we identify distinct regions in the α-z plane, where RMI corrections due to the lattice are relevant or irrelevant. We further support these findings with MPS calculations on the transverse field Ising model (TFIM). Our results, accompanied by the open-source Julia package QMICalc.jl, provide guidance to using RMI in quantum-many body physics numerical computations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, S. Dey, T. Bzdušek, and J. Maciejko
P. M. Lenggenhager, S. Dey, T. Bzdušek, and J. Maciejko
Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 076604 (2025)
– Published 15 Aug 2025
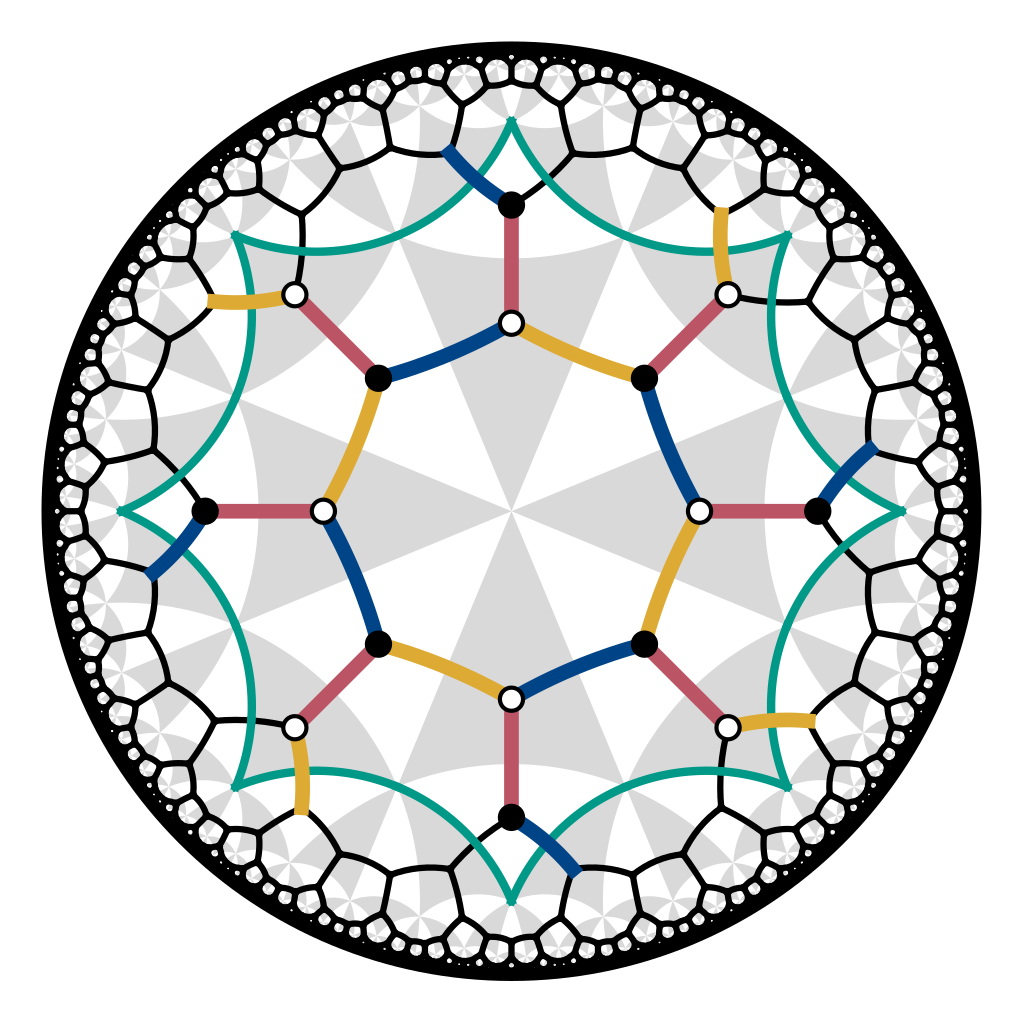
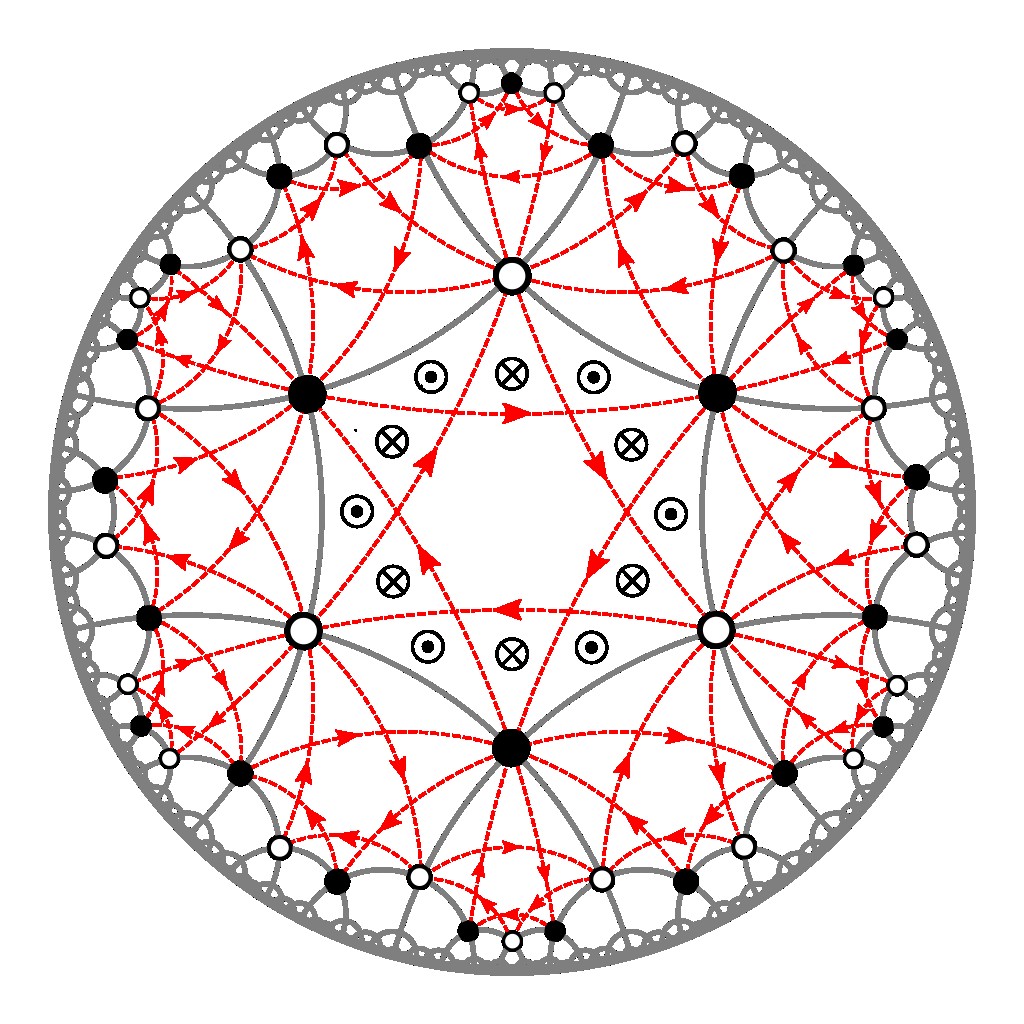
Hyperbolic lattices present a unique opportunity to venture beyond the conventional paradigm of crystalline many-body physics and explore correlated phenomena in negatively curved space. As a theoretical benchmark for such investigations, we extend Kitaev’s spin-1/2 honeycomb model to hyperbolic lattices and exploit their non-Euclidean space-group symmetries to solve the model exactly. We elucidate the ground-state phase diagram on the \(\{8,3\}\) lattice and find a gapped \(\mathbb{Z}_2\) spin liquid with Abelian anyons, a gapped chiral spin liquid with non-Abelian anyons and chiral edge states, and a Majorana metal whose finite low-energy density of states is dominated by non-Abelian Bloch states.
P. M. Lenggenhager, S. Dey, T. Bzdušek, and J. Maciejko
P. M. Lenggenhager, S. Dey, T. Bzdušek, and J. Maciejko
Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 076604 (2025)
– Published 15 Aug 2025
Hyperbolic lattices present a unique opportunity to venture beyond the conventional paradigm of crystalline many-body physics and explore correlated phenomena in negatively curved space. As a theoretical benchmark for such investigations, we extend Kitaev’s spin-1/2 honeycomb model to hyperbolic lattices and exploit their non-Euclidean space-group symmetries to solve the model exactly. We elucidate the ground-state phase diagram on the \(\{8,3\}\) lattice and find a gapped \(\mathbb{Z}_2\) spin liquid with Abelian anyons, a gapped chiral spin liquid with non-Abelian anyons and chiral edge states, and a Majorana metal whose finite low-energy density of states is dominated by non-Abelian Bloch states.
S. Dey, A. Chen, P. Basteiro, A. Fritzsche, M. Greiter, M. Kaminski, P. M. Lenggenhager, R. Meyer, R. Sorbello, A. Stegmaier, R. Thomale, J. Erdmenger, and I. Boettcher
S. Dey, A. Chen, ..., J. Erdmenger, and I. Boettcher
Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 061603 (2024)
– Published 09 Aug 2024
We demonstrate how table-top settings combining hyperbolic lattices with nonlinear dynamics universally lead to a genuine realization of the bulk-boundary-correspondence between gravity in anti-de-Sitter (AdS) space and conformal field theory (CFT). Our concrete and broadly applicable holographic toy model simulates gravitational self-interactions in the bulk and features an emergent CFT with nontrivial correlations on the boundary. We measure the CFT data contained in the two- and three-point functions and clarify how a thermal CFT is simulated through an effective black hole geometry. As a concrete example, we propose and simulate an experimentally feasible protocol to measure the holographic CFT using electrical circuits.
S. Dey, A. Chen, P. Basteiro, A. Fritzsche, M. Greiter, M. Kaminski, P. M. Lenggenhager, R. Meyer, R. Sorbello, A. Stegmaier, R. Thomale, J. Erdmenger, and I. Boettcher
S. Dey, A. Chen, ..., J. Erdmenger, and I. Boettcher
Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 061603 (2024)
– Published 09 Aug 2024
We demonstrate how table-top settings combining hyperbolic lattices with nonlinear dynamics universally lead to a genuine realization of the bulk-boundary-correspondence between gravity in anti-de-Sitter (AdS) space and conformal field theory (CFT). Our concrete and broadly applicable holographic toy model simulates gravitational self-interactions in the bulk and features an emergent CFT with nontrivial correlations on the boundary. We measure the CFT data contained in the two- and three-point functions and clarify how a thermal CFT is simulated through an effective black hole geometry. As a concrete example, we propose and simulate an experimentally feasible protocol to measure the holographic CFT using electrical circuits.
T. Tummuru, A. Chen, P. M. Lenggenhager, T. Neupert, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
T. Tummuru, A. Chen, P. M. Lenggenhager, T. Neupert, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 206601 (2024)
– Published 14 May 2024
We extend the notion of topologically protected semi-metallic band crossings to hyperbolic lattices in a negatively curved plane. Because of their distinct translation group structure, such lattices are associated with a high-dimensional reciprocal space. In addition, they support non-Abelian Bloch states which, unlike conventional Bloch states, acquire a matrix-valued Bloch factor under lattice translations. Combining diverse numerical and analytical approaches, we uncover an unconventional scaling in the density of states at low energies, and illuminate a nodal manifold of codimension five in the reciprocal space. The nodal manifold is topologically protected by a nonzero second Chern number, reminiscent of the characterization of Weyl nodes by the first Chern number.
T. Tummuru, A. Chen, P. M. Lenggenhager, T. Neupert, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
T. Tummuru, A. Chen, P. M. Lenggenhager, T. Neupert, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 206601 (2024)
– Published 14 May 2024
We extend the notion of topologically protected semi-metallic band crossings to hyperbolic lattices in a negatively curved plane. Because of their distinct translation group structure, such lattices are associated with a high-dimensional reciprocal space. In addition, they support non-Abelian Bloch states which, unlike conventional Bloch states, acquire a matrix-valued Bloch factor under lattice translations. Combining diverse numerical and analytical approaches, we uncover an unconventional scaling in the density of states at low energies, and illuminate a nodal manifold of codimension five in the reciprocal space. The nodal manifold is topologically protected by a nonzero second Chern number, reminiscent of the characterization of Weyl nodes by the first Chern number.
P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 226401 (2023)
– Published 01 Dec 2023
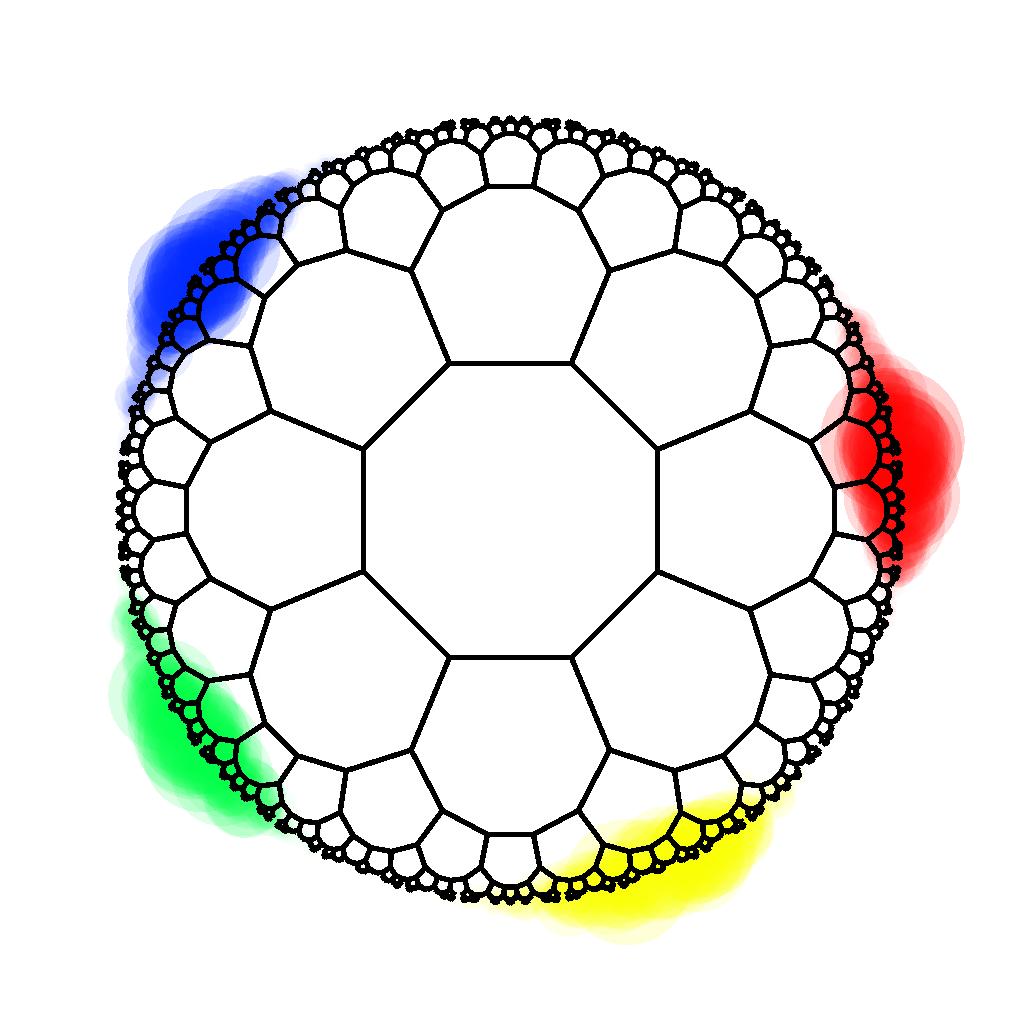
Tight-binding models on periodic lattices are commonly studied using Bloch band theory, which provides an efficient description of their energy spectra and wave functions. Besides Abelian Bloch states characterized by a momentum vector, the band theory of hyperbolic lattices involves non-Abelian Bloch states that have so far remained largely inaccessible to analytical treatments. Here, we systematically construct non-Abelian Bloch states by generalizing to hyperbolic lattices the familiar solid-state-physics notions of supercells and zone folding.
P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 226401 (2023)
– Published 01 Dec 2023
Tight-binding models on periodic lattices are commonly studied using Bloch band theory, which provides an efficient description of their energy spectra and wave functions. Besides Abelian Bloch states characterized by a momentum vector, the band theory of hyperbolic lattices involves non-Abelian Bloch states that have so far remained largely inaccessible to analytical treatments. Here, we systematically construct non-Abelian Bloch states by generalizing to hyperbolic lattices the familiar solid-state-physics notions of supercells and zone folding.
P. M. Lenggenhager
P. M. Lenggenhager
Doctoral Thesis ETH Zurich No. 29553 (2023)
– Published 29 Sep 2023
One of the cornerstones of condensed matter physics, the description of wave functions on periodic lattices in terms of energy bands of Bloch states, serves as the unifying thread in this thesis. This description is often referred to as band theory. Within its context, topological states of matter and metamaterials have taken shape as key frontiers in recent years. Related to those frontiers, this thesis delves into seemingly distinct areas: multigap topology and lattices in negatively curved space, known as hyperbolic lattices. While these two themes may appear disconnected at first, they are intrinsically tied together by concepts such as symmetry, topology, metamaterials, and the ubiquitous role of band theory.
P. M. Lenggenhager
P. M. Lenggenhager
Doctoral Thesis ETH Zurich No. 29553 (2023)
– Published 29 Sep 2023
One of the cornerstones of condensed matter physics, the description of wave functions on periodic lattices in terms of energy bands of Bloch states, serves as the unifying thread in this thesis. This description is often referred to as band theory. Within its context, topological states of matter and metamaterials have taken shape as key frontiers in recent years. Related to those frontiers, this thesis delves into seemingly distinct areas: multigap topology and lattices in negatively curved space, known as hyperbolic lattices. While these two themes may appear disconnected at first, they are intrinsically tied together by concepts such as symmetry, topology, metamaterials, and the ubiquitous role of band theory.
A. Chen, Y. Guan, P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, I. Boettcher, and T. Bzdušek
A. Chen, Y. Guan, P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, I. Boettcher, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 108, 085114 (2023)
– Published 11 Aug 2023
Particles hopping on a two-dimensional hyperbolic lattice feature unconventional energy spectra and wave functions that provide a largely uncharted platform for topological phases of matter beyond the Euclidean paradigm. Using real-space topological markers as well as Chern numbers defined in the higher-dimensional momentum space of hyperbolic band theory, we construct and investigate hyperbolic Haldane models, which are generalizations of Haldane’s honeycomb-lattice model to various hyperbolic lattices.
A. Chen, Y. Guan, P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, I. Boettcher, and T. Bzdušek
A. Chen, Y. Guan, P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, I. Boettcher, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 108, 085114 (2023)
– Published 11 Aug 2023
Particles hopping on a two-dimensional hyperbolic lattice feature unconventional energy spectra and wave functions that provide a largely uncharted platform for topological phases of matter beyond the Euclidean paradigm. Using real-space topological markers as well as Chern numbers defined in the higher-dimensional momentum space of hyperbolic band theory, we construct and investigate hyperbolic Haldane models, which are generalizations of Haldane’s honeycomb-lattice model to various hyperbolic lattices.
D. M. Urwyler, P. M. Lenggenhager, I. Boettcher, R. Thomale, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
D. M. Urwyler, P. M. Lenggenhager, I. Boettcher, R. Thomale, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 246402 (2022)
– Published 08 Dec 2022
The Bloch band theory describes energy levels of crystalline media by a collection of bands in momentum space. These bands can be characterized by non-trivial topological invariants, which via bulk-boundary correspondence imply protected boundary states inside the bulk energy gap. Recently, hyperbolic lattices that tile the negatively curved hyperbolic plane emerged as a new paradigm of synthetic matter, and their energy levels were characterized by a band structure in a four- (or higher-)dimensional momentum space. To explore the uncharted topological aspects arising in hyperbolic band theory, we here introduce elementary models of hyperbolic topological band insulators: the hyperbolic Haldane model and the hyperbolic Kane-Mele model;
D. M. Urwyler, P. M. Lenggenhager, I. Boettcher, R. Thomale, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
D. M. Urwyler, P. M. Lenggenhager, I. Boettcher, R. Thomale, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 246402 (2022)
– Published 08 Dec 2022
The Bloch band theory describes energy levels of crystalline media by a collection of bands in momentum space. These bands can be characterized by non-trivial topological invariants, which via bulk-boundary correspondence imply protected boundary states inside the bulk energy gap. Recently, hyperbolic lattices that tile the negatively curved hyperbolic plane emerged as a new paradigm of synthetic matter, and their energy levels were characterized by a band structure in a four- (or higher-)dimensional momentum space. To explore the uncharted topological aspects arising in hyperbolic band theory, we here introduce elementary models of hyperbolic topological band insulators: the hyperbolic Haldane model and the hyperbolic Kane-Mele model;
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 106, 085128 (2022)
– Published 18 Aug 2022
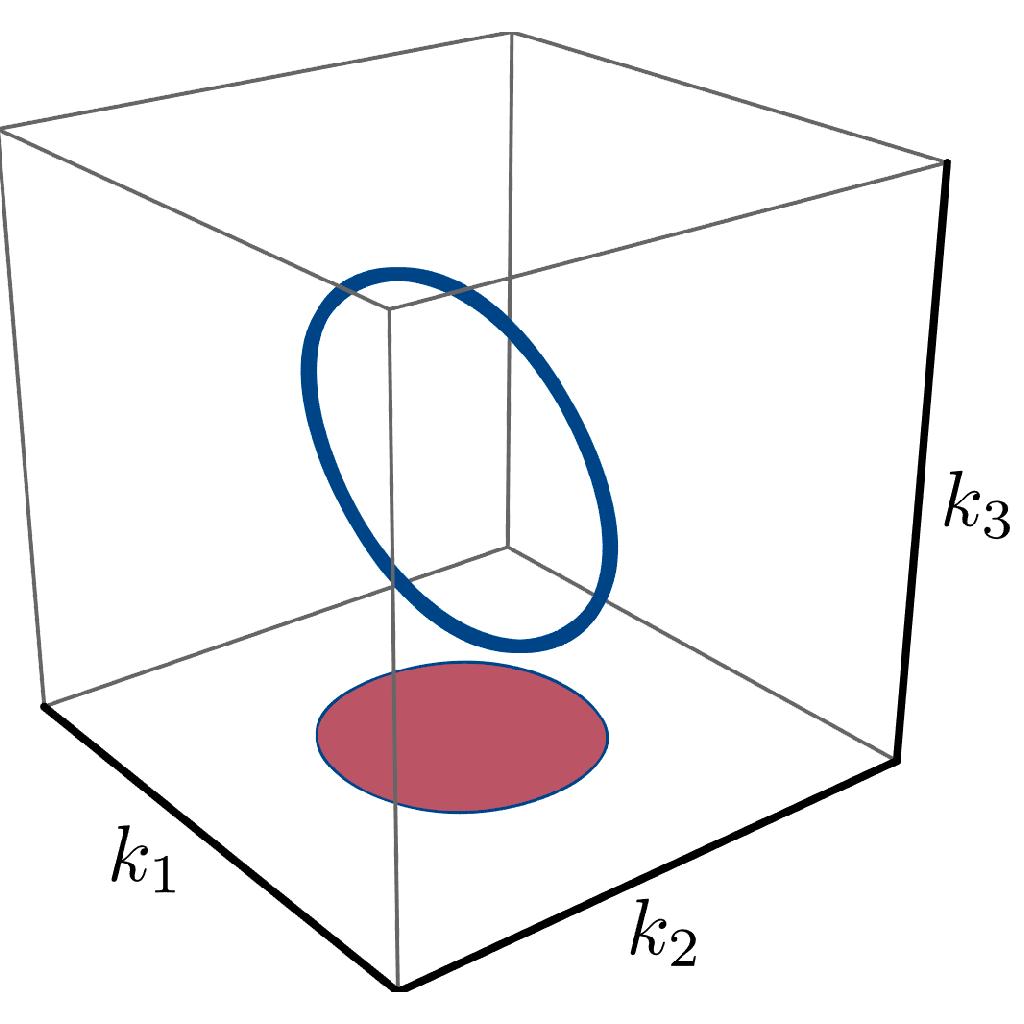
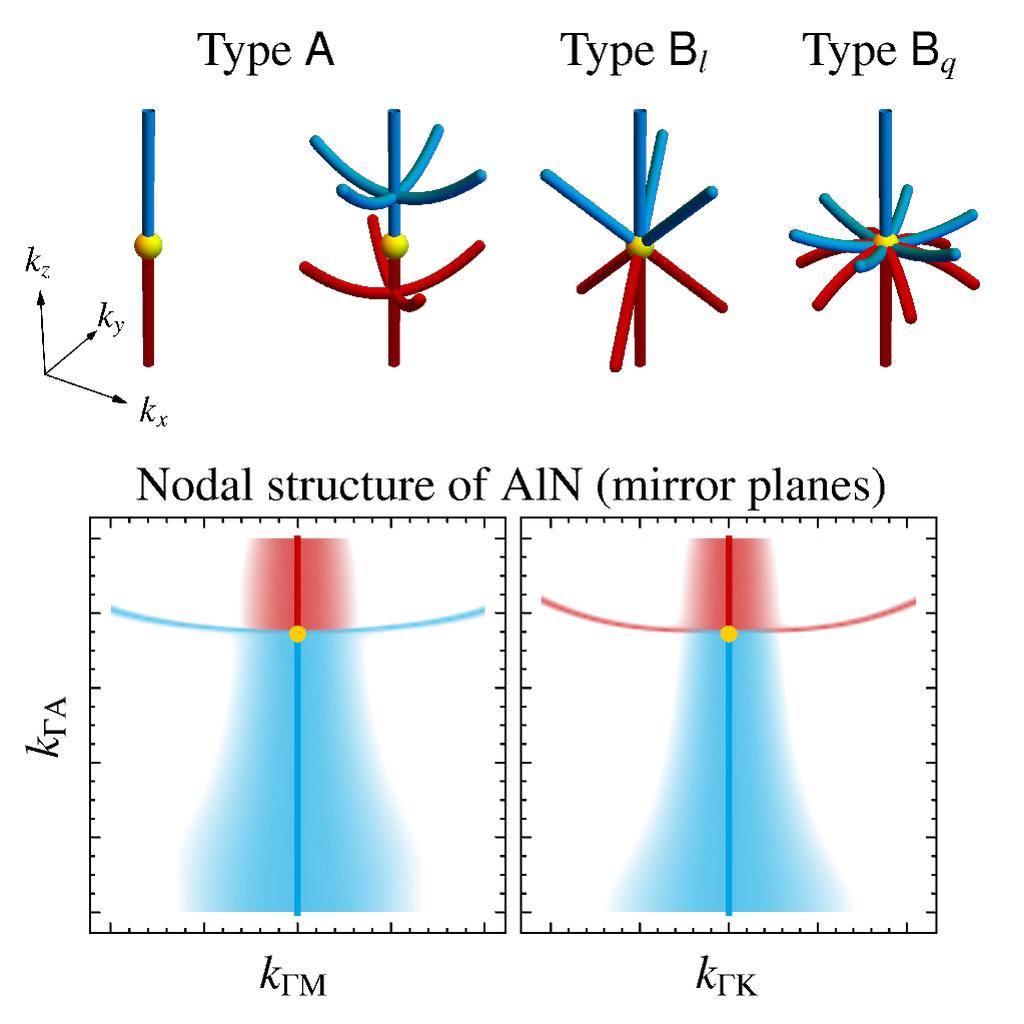
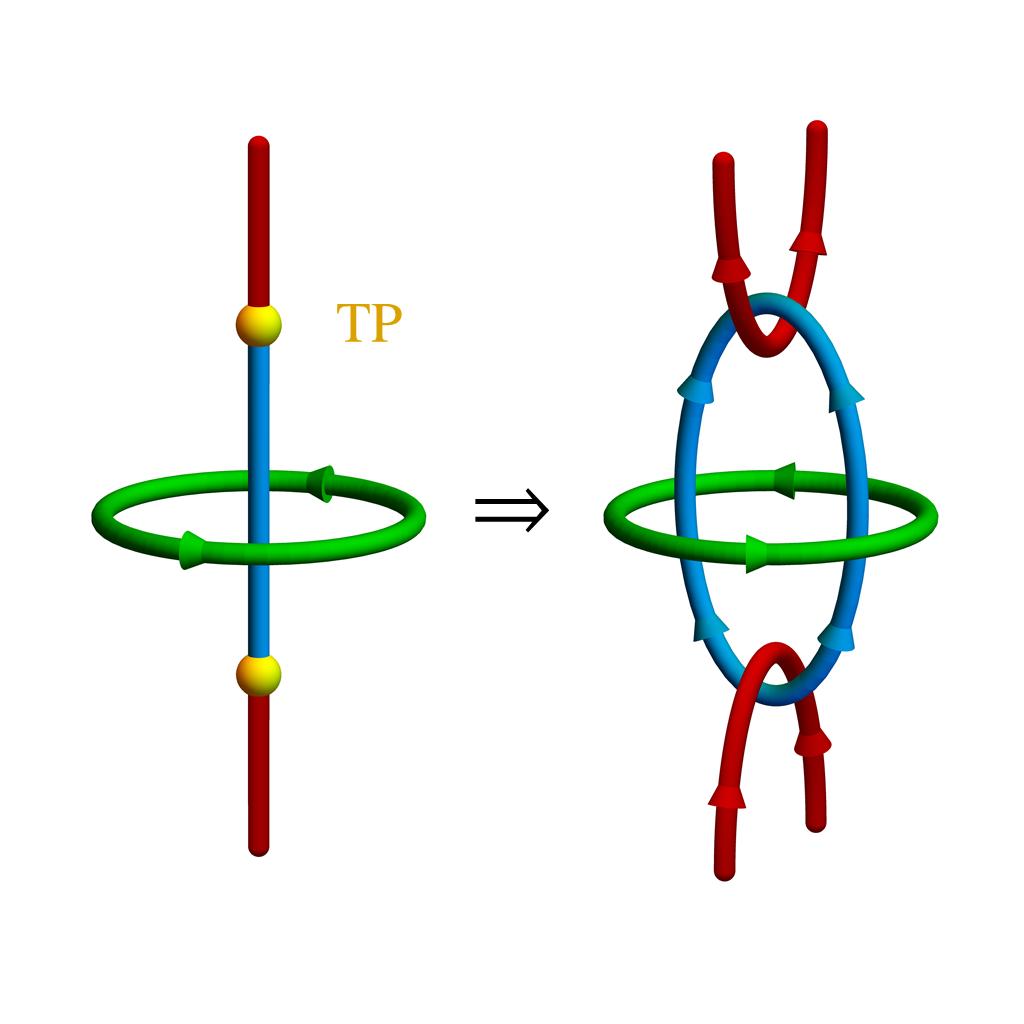
We extend the classification of three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies (triple points) to all (magnetic) space groups, including the non-symmorphic ones. The classification is based on the symmetry properties of the high-symmetry line in momentum space on which the degeneracy lies and predicts the nodal-line structure at and near the triple point. In particular, we predict the presence, number and behavior of nodal-line arcs connecting to the central nodal line (along the high-symmetry line) at nexus points. We illustrate the classification results on several material examples using first-principles calculations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 106, 085128 (2022)
– Published 18 Aug 2022
We extend the classification of three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies (triple points) to all (magnetic) space groups, including the non-symmorphic ones. The classification is based on the symmetry properties of the high-symmetry line in momentum space on which the degeneracy lies and predicts the nodal-line structure at and near the triple point. In particular, we predict the presence, number and behavior of nodal-line arcs connecting to the central nodal line (along the high-symmetry line) at nexus points. We illustrate the classification results on several material examples using first-principles calculations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 106, 085129 (2022)
– Published 18 Aug 2022
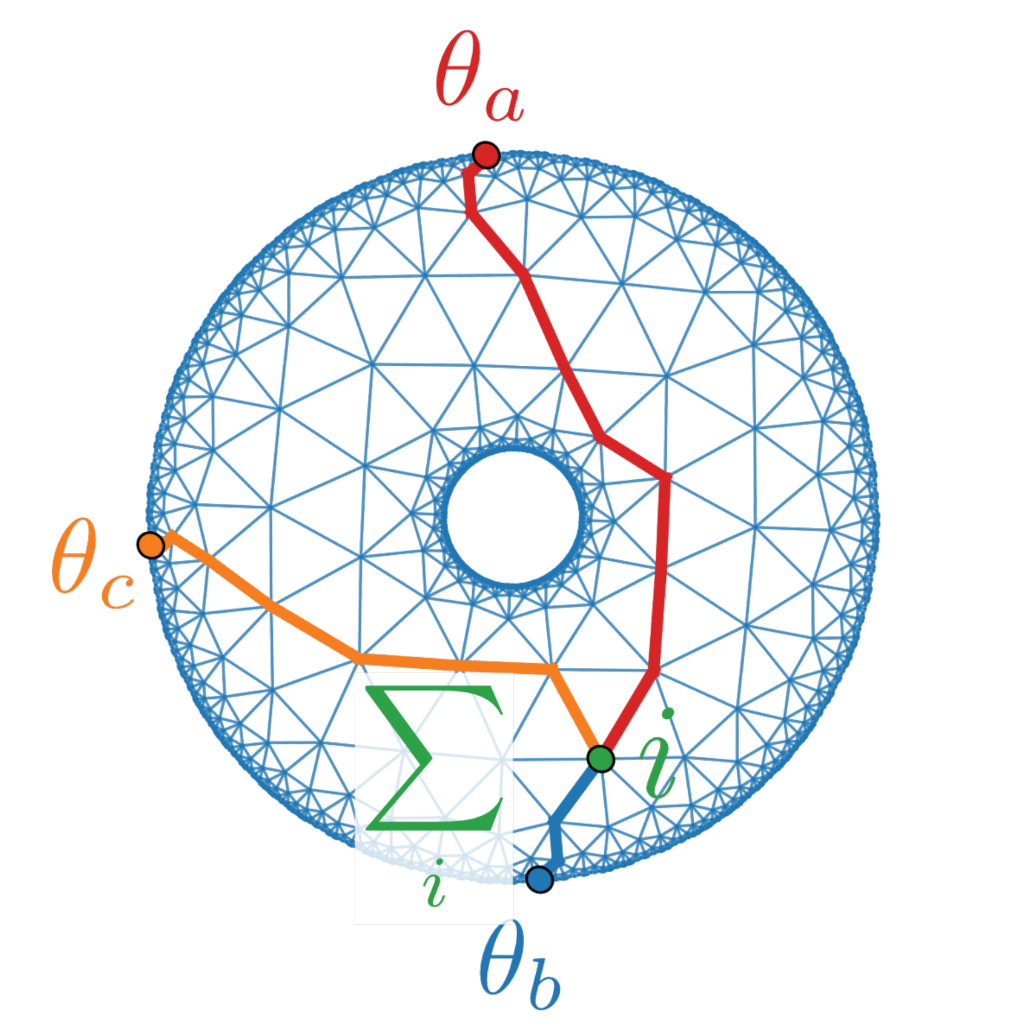
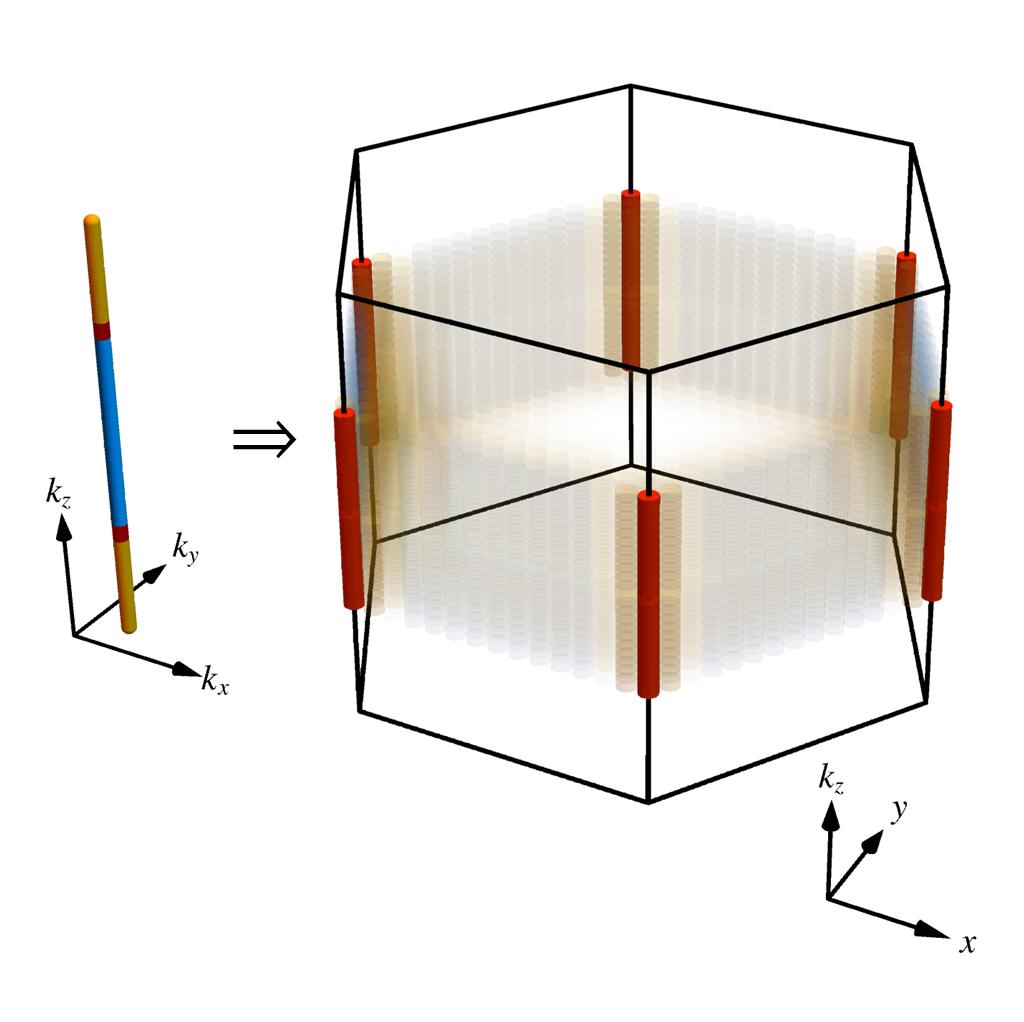
We show that pairs of triple points in systems with negligible spin-orbit coupling (three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies along high-symmetry lines) facilitate higher-topology. Our main result is a universal bulk-hinge correspondence of such pairs to fractional quantized jumps of the hinge charge as a function of the hinge-momentum. For the special case of \(\mathcal{P}\mathcal{T}\)-symmetric crystalline solids we further find that triple points are characterized by monople charges. We illustrate the derived phenomena on material examples using first-principles calculations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 106, 085129 (2022)
– Published 18 Aug 2022
We show that pairs of triple points in systems with negligible spin-orbit coupling (three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies along high-symmetry lines) facilitate higher-topology. Our main result is a universal bulk-hinge correspondence of such pairs to fractional quantized jumps of the hinge charge as a function of the hinge-momentum. For the special case of \(\mathcal{P}\mathcal{T}\)-symmetric crystalline solids we further find that triple points are characterized by monople charges. We illustrate the derived phenomena on material examples using first-principles calculations.
P. M. Lenggenhager, A. Stegmaier, L. K. Upreti, T. Hofmann, T. Helbig, A. Vollhardt, M. Greiter, C. H. Lee, S. Imhof, H. Brand, T. Kießling, I. Boettcher, T. Neupert, R. Thomale, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, A. Stegmaier, ..., T. Neupert, R. Thomale, and T. Bzdušek
Nat. Commun. 13, 4373 (2022)
– Published 28 Jul 2022
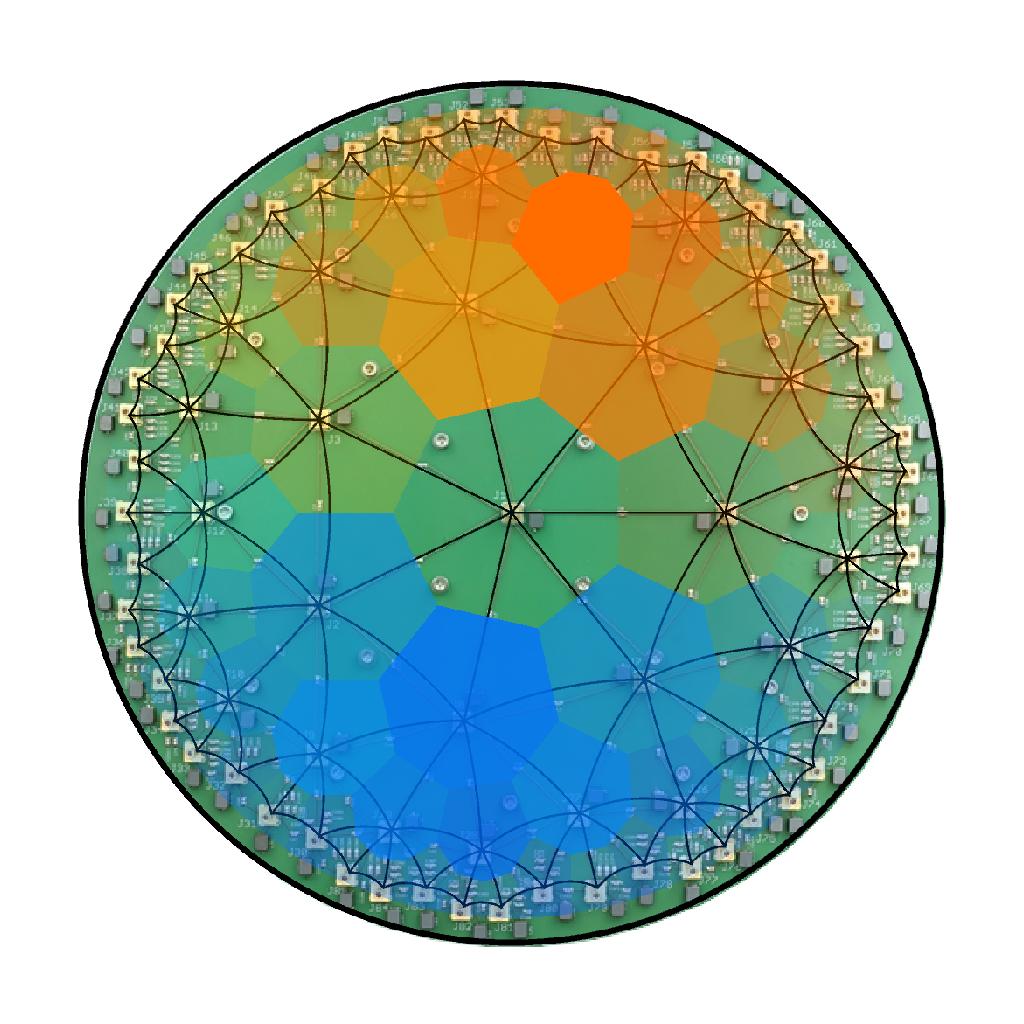
Spaces with negative curvature are particularly difficult to realize experimentally. We show how to emulate a discretized version of constant negatively curved space, a so called hyperbolic lattice, using an electric circuit network. We present static and dynamical methods which allowed us to characterize and verify the negative curvature in the implemented model. Our experiments showcase a versatile platform to emulate hyperbolic lattices in tabletop experiments, which can be utilized to explore propagation dynamics as well as to realize topological hyperbolic matter.
P. M. Lenggenhager, A. Stegmaier, L. K. Upreti, T. Hofmann, T. Helbig, A. Vollhardt, M. Greiter, C. H. Lee, S. Imhof, H. Brand, T. Kießling, I. Boettcher, T. Neupert, R. Thomale, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, A. Stegmaier, ..., T. Neupert, R. Thomale, and T. Bzdušek
Nat. Commun. 13, 4373 (2022)
– Published 28 Jul 2022
Spaces with negative curvature are particularly difficult to realize experimentally. We show how to emulate a discretized version of constant negatively curved space, a so called hyperbolic lattice, using an electric circuit network. We present static and dynamical methods which allowed us to characterize and verify the negative curvature in the implemented model. Our experiments showcase a versatile platform to emulate hyperbolic lattices in tabletop experiments, which can be utilized to explore propagation dynamics as well as to realize topological hyperbolic matter.
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, S. S. Tsirkin, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, S. S. Tsirkin, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 103, L121101 (2021)
– Published 01 Mar 2021
We classify three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies (triple points) occurring along high-symmetry lines of \(\mathcal{P}\mathcal{T}\)-symmetric crystalline solids with negligible spin-orbit coupling. By employing the recently discovered non-Abelian band topology, we argue that a rotation-symmetry-breaking strain transforms a certain class of triple points into multiband nodal links. We propose material candidates and study the consequences of this phenomenon.
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, S. S. Tsirkin, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
P. M. Lenggenhager, X. Liu, S. S. Tsirkin, T. Neupert, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. B 103, L121101 (2021)
– Published 01 Mar 2021
We classify three-fold momentum-space band structure degeneracies (triple points) occurring along high-symmetry lines of \(\mathcal{P}\mathcal{T}\)-symmetric crystalline solids with negligible spin-orbit coupling. By employing the recently discovered non-Abelian band topology, we argue that a rotation-symmetry-breaking strain transforms a certain class of triple points into multiband nodal links. We propose material candidates and study the consequences of this phenomenon.
P. M. Lenggenhager, D. E. Gökmen, Z. Ringel, S. D. Huber, and M. Koch-Janusz
P. M. Lenggenhager, D. E. Gökmen, Z. Ringel, S. D. Huber, and M. Koch-Janusz
Phys. Rev. X 10, 011037 (2020)
– Published 14 Feb 2020
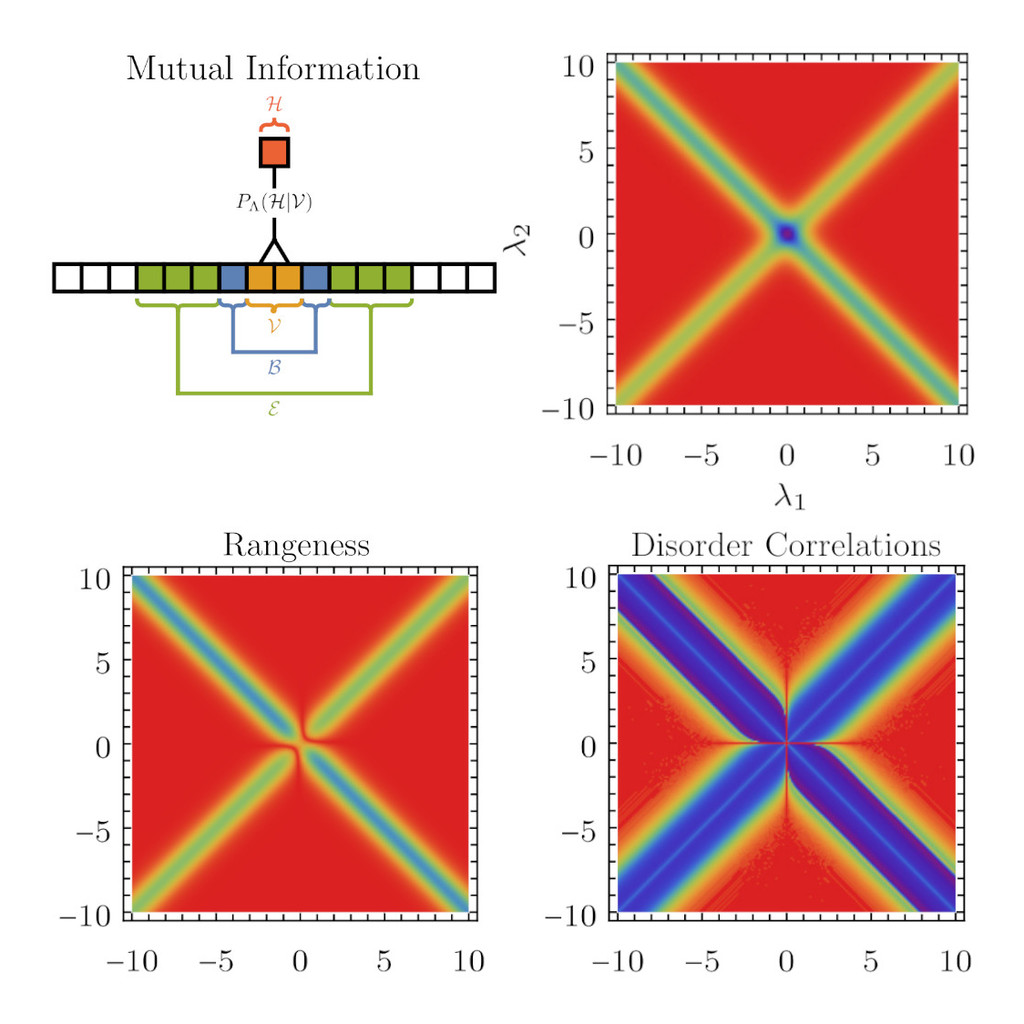
We consider a recently introduced real-space renormalization group (RG) algorithm which is based on maximizing real-space mutual information (RSMI). Based on general proofs and detailed studies of arbitrary coarse-grainings of the Ising chain, we argue that maximizing RSMI minimizes the range of interactions and, for disordered systems, correlations in the disorder distribution of the coarse-grained system.
P. M. Lenggenhager, D. E. Gökmen, Z. Ringel, S. D. Huber, and M. Koch-Janusz
P. M. Lenggenhager, D. E. Gökmen, Z. Ringel, S. D. Huber, and M. Koch-Janusz
Phys. Rev. X 10, 011037 (2020)
– Published 14 Feb 2020
We consider a recently introduced real-space renormalization group (RG) algorithm which is based on maximizing real-space mutual information (RSMI). Based on general proofs and detailed studies of arbitrary coarse-grainings of the Ising chain, we argue that maximizing RSMI minimizes the range of interactions and, for disordered systems, correlations in the disorder distribution of the coarse-grained system.