Non-Abelian hyperbolic band theory from supercells
 PDF
Supplement
Journal
arXiv
Data/Code
PDF
Supplement
Journal
arXiv
Data/Code
P. M. Lenggenhager, J. Maciejko, and T. Bzdušek
Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 226401 (2023) – Published 01 Dec 2023

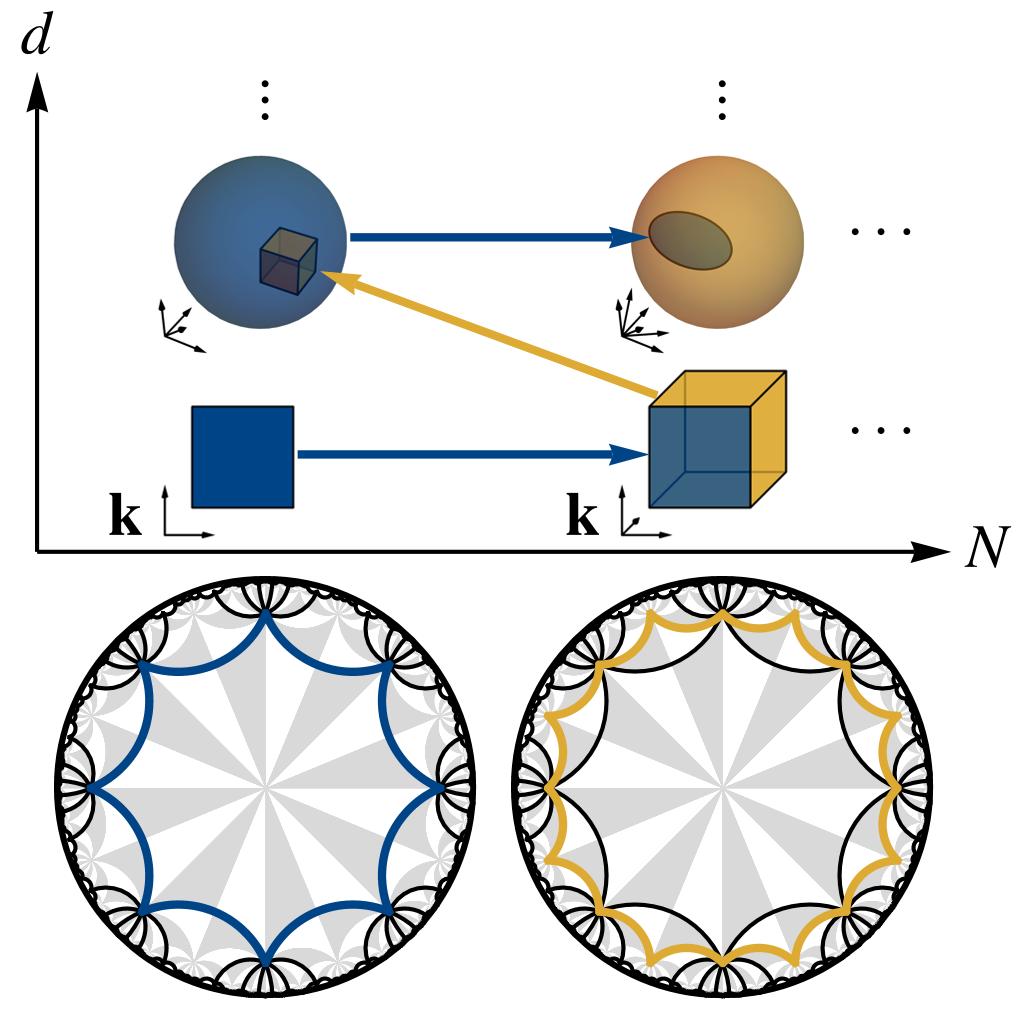
Tight-binding models on periodic lattices are commonly studied using Bloch band theory, which provides an efficient description of their energy spectra and wave functions. Besides Abelian Bloch states characterized by a momentum vector, the band theory of hyperbolic lattices involves non-Abelian Bloch states that have so far remained largely inaccessible to analytical treatments. Here, we systematically construct non-Abelian Bloch states by generalizing to hyperbolic lattices the familiar solid-state-physics notions of supercells and zone folding. By applying Abelian hyperbolic band theory to sequences of supercells, constructed recursively as symmetric aggregates of multiple smaller cells, we numerically compute the density of states of several elementary and topological tight-binding models and observe rapid convergence with increasing supercell size, for both gapless and gapped models. We propose our supercell method as a first step towards a complete band-theoretic characterization of hyperbolic lattices and an efficient means of approximating the thermodynamic limit. We make our algorithms publicly available in a software package to facilitate future studies of hyperbolic quantum matter.
Check out this Wolfram community post which has been selected for the editorial columns Staff Picks and Publication Materials. In that post, I demonstrate how to use our Mathematica package HyperBloch to easily apply the supercell method to various tight-binding models and to visualize those models.