Computational access to lattice and long-wavelength physics in quantum mutual information
 PDF
arXiv
PDF
arXiv
P. M. Lenggenhager, M. M. Denner, D. E. Gökmen, M. Koch-Janusz, T. Neupert, M. H. Fischer
arXiv:2510.02466 (2025) – Uploaded 06 Oct 2025

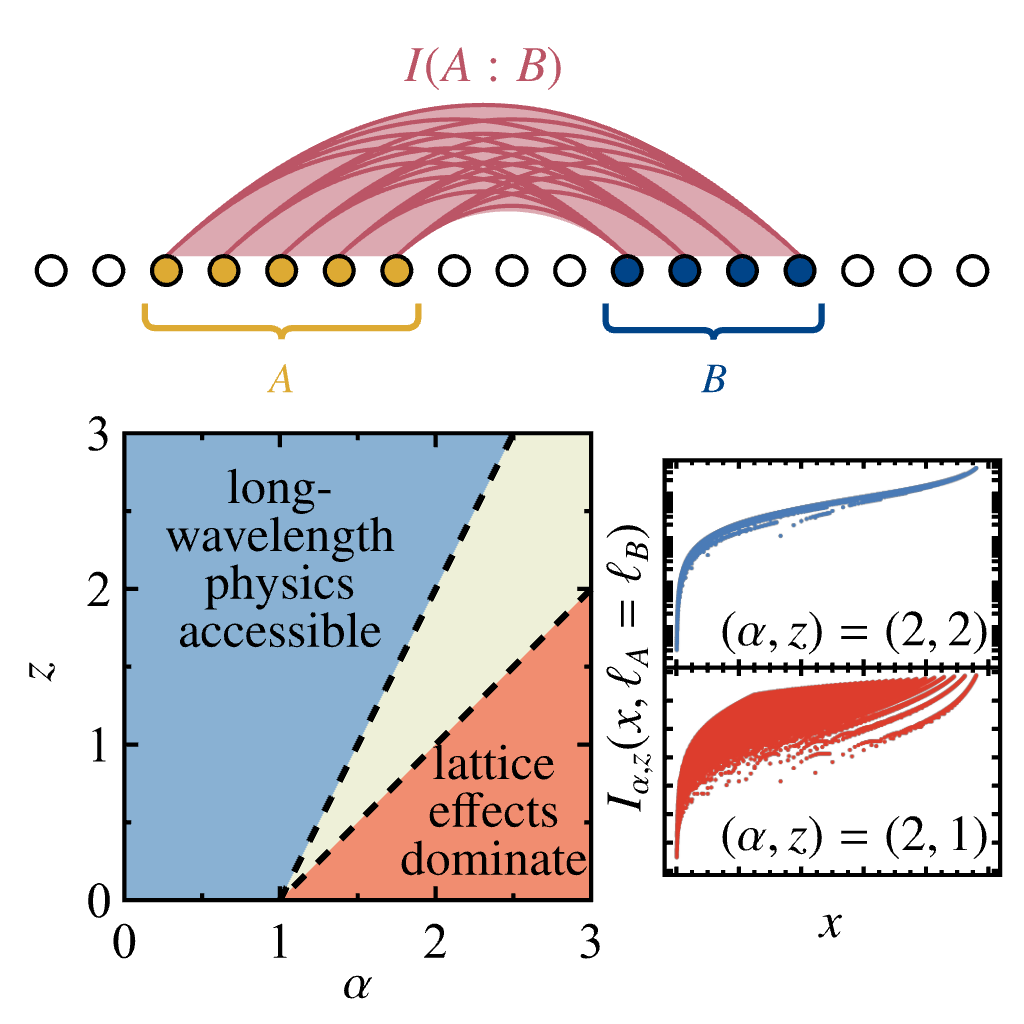
Quantum mutual information is an important tool for characterizing correlations in quantum many-body systems, but its numerical evaluation is often prohibitively expensive. While some variants of Rényi Mutual Information (RMI) are computationally more tractable, it is not clear whether they correctly capture the long-wavelength physics or are dominated by UV effects, which is of key importance in lattice simulations. We analyze the relevance of lattice effects on the family of α-z Rényi mutual informations for ground states of models with conformal field theory descriptions. On the example of massless free fermions we identify distinct regions in the α-z plane, where RMI corrections due to the lattice are relevant or irrelevant. We further support these findings with MPS calculations on the transverse field Ising model (TFIM). Our results, accompanied by the open-source Julia package QMICalc.jl, provide guidance to using RMI in quantum-many body physics numerical computations.